Investor Psychology: How to Think Like a VC and Secure Funding
Securing funding from venture capitalists (VCs) is a challenging endeavor.
Securing funding from venture capitalists (VCs) is a challenging endeavor. To increase their chances of success, entrepreneurs must understand the psychology of investors, their decision-making process, and the criteria they use to evaluate opportunities. This article explores the intricacies of investor psychology, providing entrepreneurs with the knowledge and tools to navigate the VC landscape effectively.
Key Takeaways
-
Understand VCs' focus on high-growth potential, strong teams, and risk mitigation.
-
Deliver a concise pitch deck with a clear problem, solution, and strong team.
-
Build authentic relationships with VCs by networking and providing consistent updates.
-
Conduct thorough research, have realistic valuations, and prioritize team expertise.
Understanding the VC Mindset
Venture capitalists are strategic partners who seek to maximize returns by identifying and supporting high-growth companies. To secure VC funding, entrepreneurs must understand the factors driving these investment decisions.
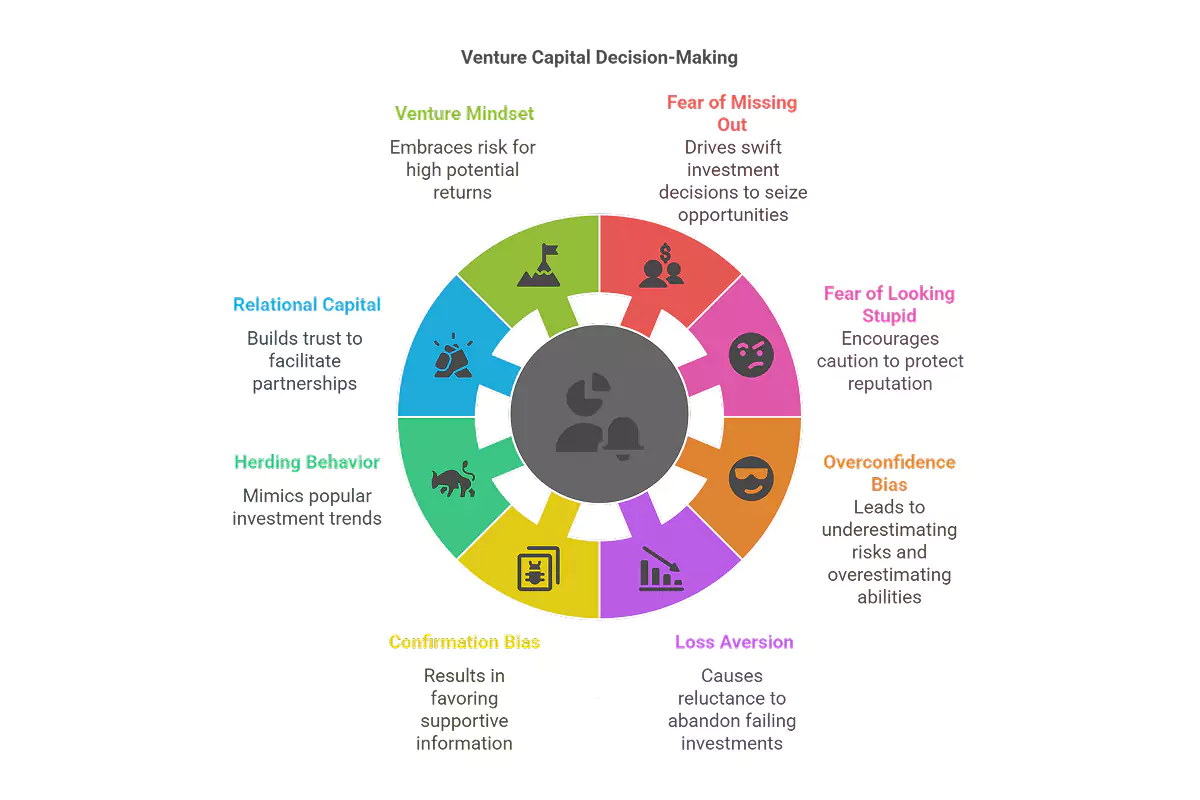
"At the heart of VC decision-making lie two primary psychological drivers: the fear of missing out (FOMO) and the fear of looking stupid (FOLS)."
Fear and Greed: The Driving Forces
At the heart of VC decision-making lie two primary psychological drivers: the fear of missing out (FOMO) and the fear of looking stupid (FOLS). FOMO compels investors to seize promising opportunities swiftly, while FOLS makes them cautious and hesitant to make decisions that could jeopardize their reputation. These seemingly conflicting forces create a dynamic where VCs seek secure deals with the potential for substantial returns.
Cognitive Biases
VCs, like all humans, are susceptible to cognitive biases that can cloud their judgment. Some common biases include:
-
Overconfidence Bias: Past successes can sometimes lead to an inflated sense of ability, causing investors to underestimate risks and overestimate their ability to pick winners.
-
Loss Aversion: The tendency to avoid losses more than seeking equivalent gains can make investors hold onto failing investments for too long, hoping for a turnaround that may never come.
-
Confirmation Bias: This bias leads investors to favor information confirming their beliefs while overlooking contradictory evidence, potentially leading to flawed decisions.
-
Herding Behavior: Following the crowd and mimicking the investment decisions of other VCs, particularly those with strong reputations, can contribute to market bubbles and, ultimately, poor investment choices.
Relational Capital
Beyond financial metrics and due diligence, relational capital is significant in securing VC funding. Building trust and rapport with VCs can reduce their vigilance and facilitate partnerships. When investors trust entrepreneurs, they are likelier to believe in their vision and commit capital.
The Venture Mindset
The venture mindset is characterized by a high tolerance for risk, a willingness to embrace uncertainty, and a focus on potential rather than immediate returns. VCs operate in an environment where failure is common, and they prioritize "home runs" – investments that generate outsized returns – over avoiding strikeouts. This mindset allows them to make bold decisions and invest in companies that others might overlook.
The VC Decision-Making Process
The VC decision-making process is a multi-faceted evaluation that involves several key steps:
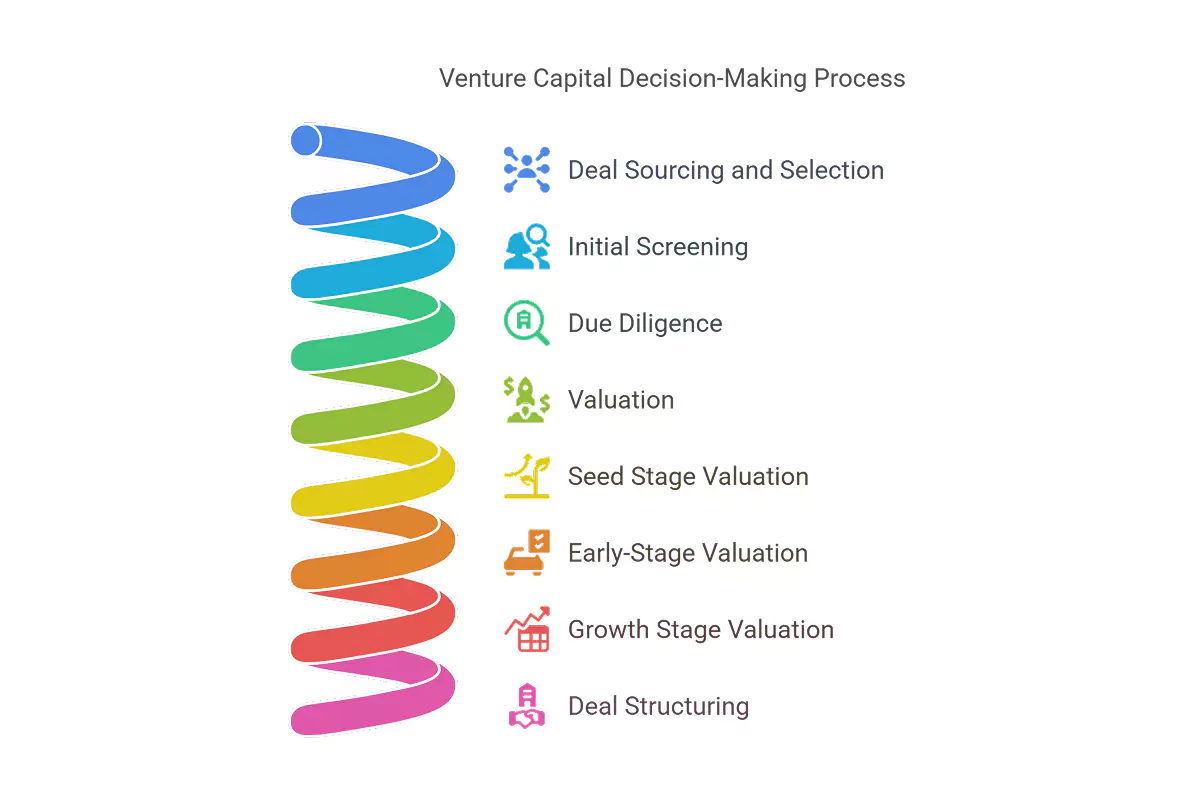
“VCs rely heavily on their networks to source deals, evaluating hundreds of companies each year, but only a small fraction receive funding."
Deal Sourcing and Selection
VCs rely heavily on their networks to source deals, evaluating hundreds of companies each year, but only a small fraction receive funding. The initial screening process focuses on identifying companies with innovative products or services, large market potential, and strong leadership teams.
Due Diligence
Once a company passes the initial screening, VCs conduct extensive due diligence. This involves a thorough analysis of the business model, financials, legal structure, competitive landscape, and management team. The goal is to identify potential risks and assess the company's ability to execute its plan.
Valuation
Determining a company's valuation is a crucial step in the investment process. VCs use various methods to assess a startup's worth, including cash-on-cash multiples, internal rate of return (IRR), and net present value (NPV). They also consider qualitative factors like the anticipated exit strategy and the company's potential for future growth.
The stage of investment—whether it's seed, early-stage, or growth—plays a pivotal role in venture capital decision-making1.
- Seed Stage: Valuation at this stage is often more art than science, as there are limited financials. It may rely heavily on the team's background, market potential, and the uniqueness of the product.
💡Free Resources: Crafting Seed to Series A Pitch Deck: A Slide-by-Slide Guide
-
Early-Stage: Companies have some track record, allowing for more traditional finance methods in valuation. Valuations might adjust for the technology risk and market adoption risks that are still prevalent.
-
Growth Stage: Companies typically have clearer financial trajectories. Venture capitalists focus on detailed financial analyses, forecasting revenues and growth to inform valuations.
Deal Structuring
After determining the valuation, VCs structure the deal to align interests and mitigate risks. This may involve milestone-based financing, equity ownership, or other terms that protect the investor's investment while incentivizing the company's performance.
Post-Investment Value-Added Services
VCs often provide more than just capital. They leverage their expertise and networks to support their portfolio companies. This can include strategic advice, operational support, and assistance with future funding rounds.
Key Criteria for Evaluation
While the specific criteria vary between VCs and investment stages, some common factors influence their decisions:

"A strong team is essential for building a successful company, and VCs prioritize investing in people as much as ideas."
Management Team
The management team is arguably the most important factor VCs consider. They look for experienced, adaptable, and passionate leaders who can execute the business plan and navigate challenges. A strong team is essential for building a successful company, and VCs prioritize investing in people as much as ideas.
Beyond experience and adaptability, VCs seek founders who are fully committed to the enterprise, open to advice, and possess strong communication skills and passion for their product or service8.
Market Opportunity
VCs seek companies that address large and growing markets. The size of the market determines the potential upside for an investment, and VCs typically look for opportunities with a total addressable market (TAM) of $1 billion or more.
However, it's important to note that focusing on a niche market can also be a successful strategy. Many successful companies, like Uber and Facebook, started by targeting specific niche audiences before expanding to larger markets.
Business Model
A clear and scalable business model is crucial for attracting VC funding. VCs want to understand how the company generates revenue, acquires customers, and plans to scale its operations effectively.
A key aspect of a strong business model is demonstrating positive unit economics, meaning the company can generate profit at the individual customer level. This indicates a sustainable and scalable business.
Product or Technology
The strength and uniqueness of the product or service are also important considerations. VCs look for offerings with a competitive edge, intellectual property protection, and the potential to disrupt the market.
Intellectual property (IP) protection, such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights, can significantly enhance a startup's value proposition. Strong IP protection can create barriers to entry for competitors and safeguard innovation.
Traction and Proof of Concept
VCs often prefer startups with demonstrated traction or a proven concept. This can include a growing customer base, validated product-market fit, or a minimum viable product (MVP). Evidence of early success increases confidence in the company's potential.
Traction can be demonstrated through various metrics, such as revenue growth, user acquisition, and partnerships. These metrics provide tangible evidence of market demand and the company's ability to execute its plan.
Financial Projections and Exit Strategy
VCs carefully evaluate a startup's financial projections, including revenue forecasts, cost structures, and expected profitability. They also consider the potential exit strategies, such as acquisition or initial public offering (IPO), and the likelihood of generating significant returns.
VCs prioritize investments that offer clear paths to liquidity, known as liquidity events. Acquisitions and IPOs are common liquidity events that allow VCs to realize returns on their investments.
Risk Assessment
VCs conduct thorough risk assessments to evaluate the potential downsides of an investment. They consider various types of risks, including:
-
Market Risks: These include risks associated with market acceptance, competition, and economic conditions.
-
Execution Risks: These relate to the company's ability to execute its business plan effectively.
-
Regulatory Risks: These involve potential legal or regulatory challenges that could impact the company's operations.
-
Financial Risks: These relate to the company's financial stability and ability to manage its finances effectively.
Geographical Considerations
When evaluating potential investments, geography often influences VCs' decisions. Factors like proximity to key markets and the availability of skilled labor play significant roles.
Economic and Market Trends
Prevailing economic and market trends also influence VC investment decisions. Market capitalization and research and development spending are critical metrics.
Common Mistakes Entrepreneurs Make
Understanding the common pitfalls can help entrepreneurs avoid them and increase their chances of securing funding.
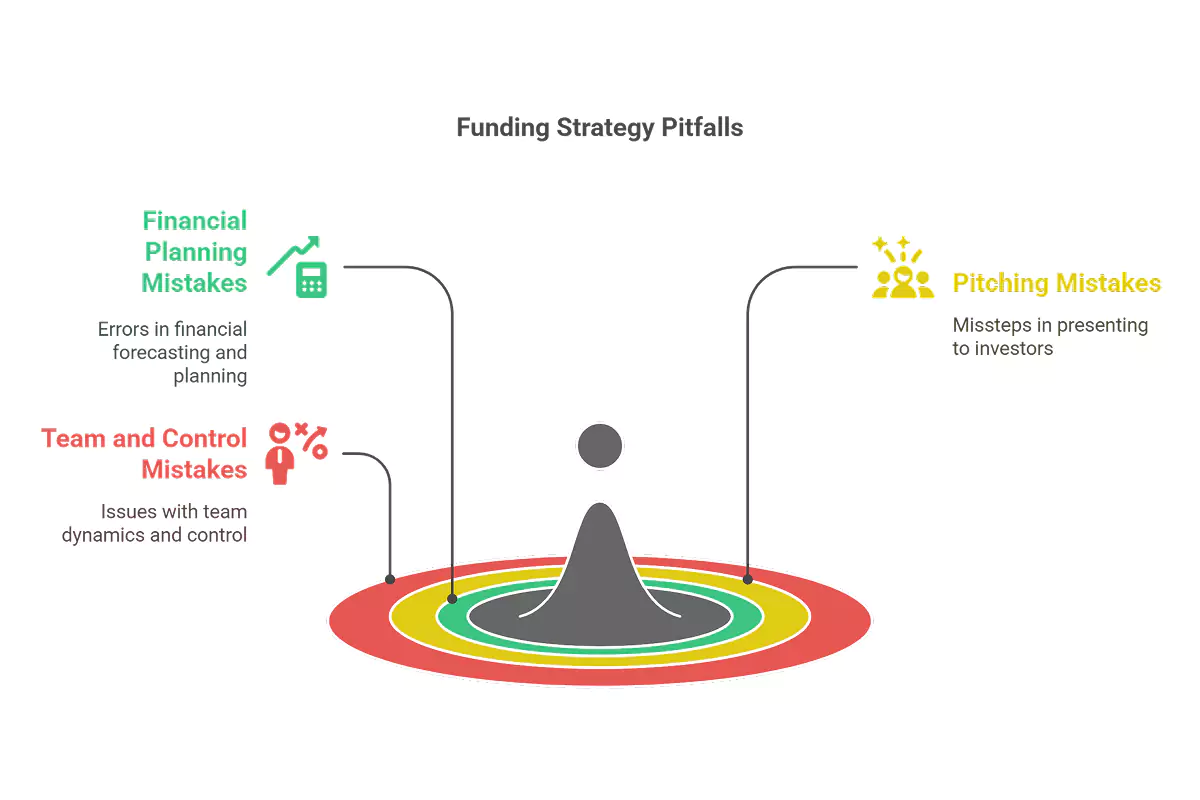
"Success in securing funding isn’t just about having a groundbreaking idea—it’s about meticulous preparation, from understanding your financials and market to choosing the right investors and maintaining control of your vision."
Financial Planning Mistakes
-
Failing to Understand Their Financial Outlook: Entrepreneurs need a solid grasp of their financial projections and a well-prepared financial model to demonstrate viability and growth potential. This includes having a detailed financial plan with realistic income and expense forecasts.
-
Demonstrating Poor Timing in Securing Funding: Timing is crucial when seeking funding. Securing funding too early can lead to unnecessary debt, while securing it too late can hinder growth.
Pitching Mistakes
-
Pitching to the Wrong Investors: Not all investors are the same. Entrepreneurs should research different types of investors by stage and space and tailor their pitch accordingly.
-
Being Unprepared to Ask for Support: Entrepreneurs should be comfortable asking for money and have a clear plan for how they will use the funds to achieve their goals.
-
Lack of Research and Preparation: Approaching VCs without thorough research and preparation is a major mistake. Entrepreneurs should understand the VC firm's investment thesis, portfolio companies, and preferred industry sectors.
-
Lack of Clarity in the Business Model: Entrepreneurs should clearly articulate their business model, including how they generate revenue, their target customers, and their scaling plans.
-
Unrealistic Valuation Expectations: Setting unrealistic valuation expectations can deter investors. Entrepreneurs should conduct thorough valuation analysis and be open to negotiation.
-
Lack of Traction or Proof of Concept: VCs typically seek startups with some traction or a proven concept. Entrepreneurs should have a solid customer base, validated product-market fit, or an MVP.
Team and Control Mistakes
-
Overlooking the Team: VCs invest in people as much as ideas. Entrepreneurs should highlight their team's expertise, track record, and ability to execute the business plan.
-
Relying Too Much on Friends and Family: While friends and family can be a source of early-stage funding, entrepreneurs should seek investors with relevant skills and expertise who can add value beyond capital.
-
Relinquishing Control of the Business: Entrepreneurs should carefully consider the implications of different funding options and the potential impact on their decision-making authority. Giving up too much equity or control can be detrimental in the long run.
💡Free Resources: 5 Reasons Why Startups Fail at Fundraising (And How to Fix It)
Effectively Pitching to VCs
A successful pitch requires a compelling narrative, a clear understanding of the VC's perspective, and a data-driven approach.
Delivering a Compelling Pitch
-
Explain the opportunity clearly and concisely in the first five minutes.
-
Make the pitch interactive and engaging.
-
Avoid reading from the deck.
-
Treat the meeting as a mutual evaluation.
-
Brag about the team and their expertise.
-
Be bold and ambitious in your vision.
-
Be specific about your target market.
-
Know your competition and what sets you apart.
-
Admit what you don't know and be willing to follow up.
-
Tailor your story to the investor and stage of your company.
-
Convey confidence and inevitability in your vision.
💡Free Resources: How to Create an Unignorable Startup Pitch Deck
Building a Compelling Pitch Deck
A well-structured pitch deck is essential for capturing investors' attention and conveying your message effectively. It should be concise, ideally around 12-15 slides. Key elements include:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Company Purpose | Define your mission and vision clearly. This serves as an anchor point for your pitch and guides your company's direction. |
| Problem | Highlight the market problem your startup addresses. Clearly convey the scope and relevance of the problem to capture investors' attention. |
| Solution | Showcase your product or service as the ideal solution to the problem. Highlight your solution's unique features and benefits to convince investors of its value. |
| Market Size and Opportunity | Outline the market potential and growth opportunities. |
| Competition | Identify your key competitors and highlight your unique advantages. |
| Product | Provide a detailed look at your product, including its features and benefits. |
| Business Model | Explain your revenue generation strategy and customer acquisition plan. |
| Team | Showcase the experience and expertise of your team members. |
| Financials and Key Metrics | Share crucial financial data and growth metrics. |
Utilizing Pitch Deck Analysis Tools
Entrepreneurs can leverage AI-powered tools like Evalyze.ai to analyze their pitch decks and receive expert feedback. Evalyze provides a comprehensive score that indicates how prepared your pitch deck is for real investor meetings, along with actionable improvements.
💡Free Resources: Use AI for Fundraising
Building and Maintaining Relationships with VCs
Building strong relationships with VCs is crucial for securing funding and ongoing support.
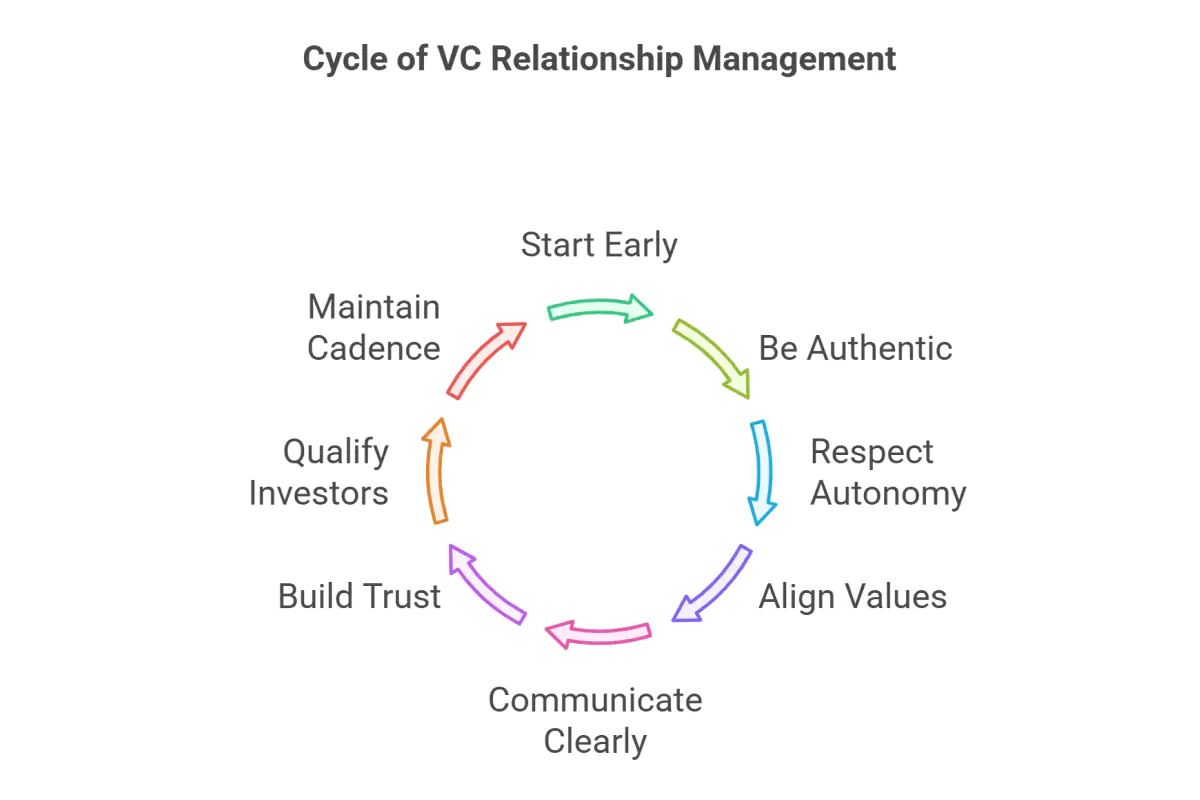
"Building strong relationships with VCs is not just about securing funding—it's about fostering trust, transparency, and long-term partnerships that support mutual growth."
Building Relationships
-
Start Early and Be Helpful: Building relationships with VCs is most effective when you start early, before actively seeking funding. This allows you to demonstrate your interest and expertise, offer valuable feedback, and provide introductions and resources.
-
Be Authentic and Transparent: Honesty and transparency are key to building trust. Be upfront about your intentions, expectations, and capabilities.
-
Respect Their Autonomy and Decisions: Respect VCs' autonomy and decisions, even if you don't always agree. Recognize that they are strategic partners, not just sources of capital.
-
Align on Values and Expectations: Mismatched values can lead to issues. Ensure alignment on values and set clear expectations for communication and working processes.
-
Establish Clear Communication Channels: Set expectations for communication frequency and channels to prevent misunderstandings.
-
Build Trust and Transparency: Open and honest communication fosters trust and strengthens the relationship.
-
Ask Questions to Qualify Potential Investors: Use open-ended questions to assess whether an investor is a good fit for your startup.
-
Don't Burn Bridges: Maintain positive relationships with VCs, even after a rejection, as they may open doors for you later.
-
Ask for Referrals: Leverage your VC network to get introductions to other investors.
-
Conduct Informational Interviews: Informational interviews can help you learn more about the industry and build relationships with VCs.
-
Utilize Cold Outreach: Research VCs, keep your message concise, and follow up appropriately when reaching out to those you don't know.
-
Understand Your Value Proposition: Clearly articulate your skills and experience to build stronger relationships.
-
Understand the Importance of Cultural Fit: Aligning with a VC firm's culture and values can contribute to a successful relationship.
Maintaining Relationships
-
Maintain a Consistent Cadence of Communication: Provide regular updates and maintain consistent communication, even after securing funding.
-
Avoid Oversharing or Undersharing Information: Maintain a balanced approach to information sharing to build trust.
-
Be Early for Meetings and Send Follow-Up Emails: Demonstrate professionalism and respect for the investor's time.
-
Remember That Investors Are People Too: Build personal connections and understand investors' perspectives.
Synthesizing the VC Mindset
To effectively secure VC funding, entrepreneurs must synthesize the key takeaways from understanding investor psychology and the VC decision-making process. This involves:
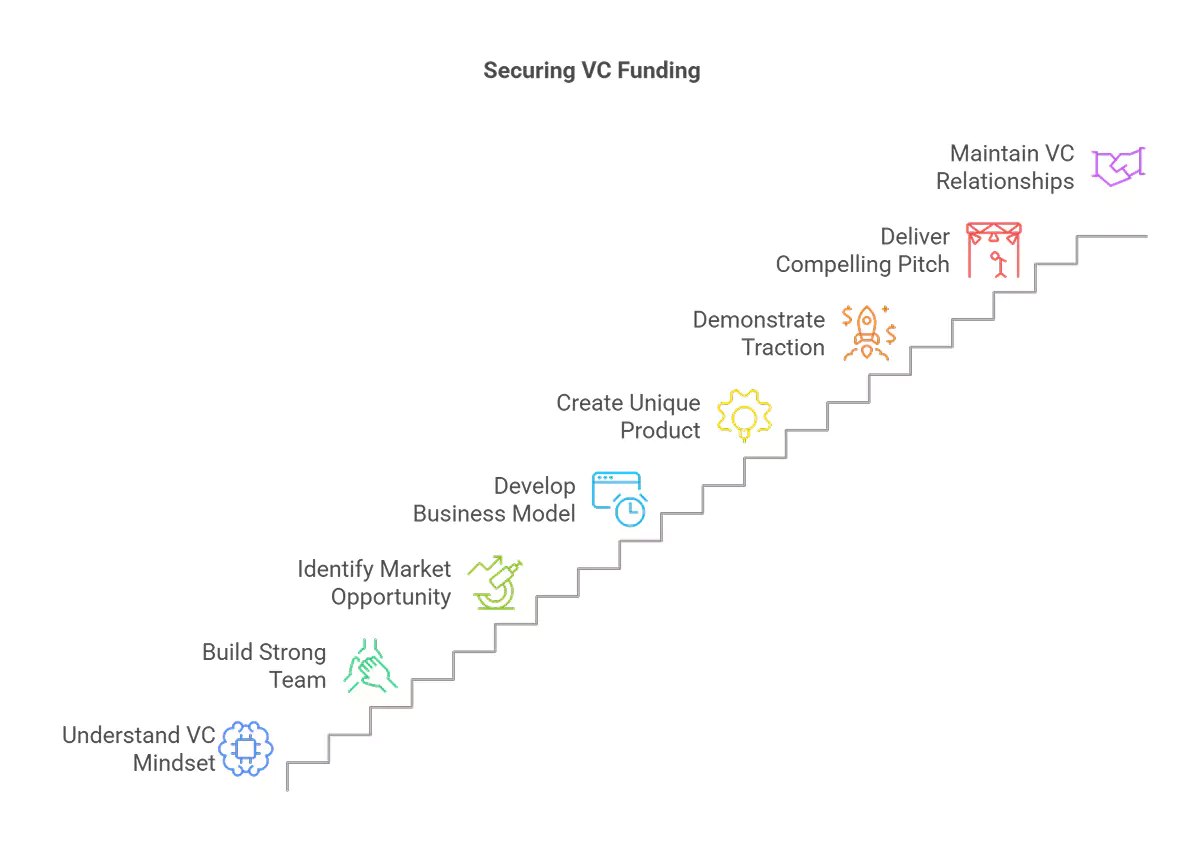
-
Developing a deep understanding of the VC mindset: Recognize that both FOMO and FOLS drive VCs, and they seek high-growth opportunities with the potential for significant returns.
-
Building a strong and passionate team: Assemble a team with the experience, adaptability, and commitment to execute the business plan and navigate challenges.
-
Identifying a large and growing market opportunity: Focus on a market with significant potential for growth and clearly articulate how your company will capture a meaningful share.
-
Developing a clear and scalable business model: Demonstrate how your company generates revenue, acquires customers, and plans to scale its operations effectively.
-
Creating a unique and defensible product or technology: Develop a product or service with a competitive edge, intellectual property protection, and the potential to disrupt the market.
-
Demonstrating traction and proof of concept: Provide evidence of early success through metrics like revenue growth, user acquisition, and partnerships.
-
Creating a compelling pitch deck and delivering a confident pitch: Craft a concise and engaging pitch deck that tells a story and highlights your company's strengths. Deliver your pitch confidently and clearly, tailoring your message to the specific investor.
-
Building and maintaining strong relationships with VCs: Start building relationships early, be authentic and transparent, and maintain consistent communication.
💡Free Resources: Fundraising 101: How to Raise Your First Round
Conclusion
You can boost your chances of success by addressing key pitfalls—like unclear value propositions, weak financials, or poor networking.
Tools like Evalyze.ai streamline this process, offering data-driven insights and pitch optimization to help you stand out.
Don’t let common mistakes hold you back—use Evalyze.ai to build trust with investors and secure your startup's funding for long-term growth.
More Articles
Evalyze Features: Assess Your Pitch Performance
A well-structured pitch deck is essential for startups seeking to attract investor interest and secure funding.
September 5, 2024
Evalyze's 6 Critical Assessment Criteria
Evalyze is your AI-powered pitch deck advisor. It helps startups refine their pitches and secure funding by providing expert feedback and actionable insights.
November 1, 2024